How to Identify USB-C 2.0, 3.0, and 4.0 from Connector Design on a Drawing
How to Identify USB-C 2.0, 3.0, and 4.0 from Connector Design on a Drawing?
How to Identify USB-C 2.0, 3.0, and 4.0 from Connector Design on a Diagram
USB-C connectors differ across versions (USB 2.0, USB 3.0, and USB 4.0) in their pin configurations. By analyzing the design on a diagram, you can determine the specific version of USB-C. Here are the key distinctions:
1. USB-C 2.0 Pin Configuration
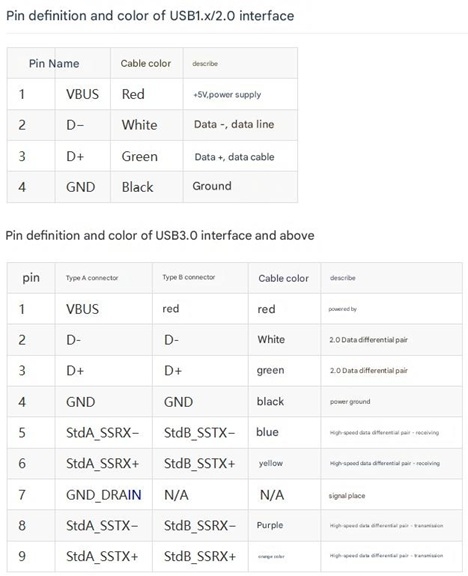
Minimal pin count: Only 4 main pins (Vbus, GND, D+, D-).
No high-speed differential signal lines, supports a 480 Mbps transfer speed.
No TX/RX differential pairs, meaning no support for higher data rates.
2. USB-C 3.0 (or 3.1 Gen 1) Pin Configuration
Includes SuperSpeed TX/RX differential signal pairs (TX1+/TX1-, RX1+/RX1-) in addition to USB 2.0 pins.
Total of 9-12 functional pins, supporting 5Gbps or 10Gbps speeds depending on the version.
Enhanced Vbus/GND pins to support improved power delivery.
3. USB-C 4.0 Pin Configuration
Full 24-pin design, including all USB 3.0 pins plus additional TX2+/TX2-, RX2+/RX2- differential pairs.
Supports 20Gbps or 40Gbps ultra-high-speed data transmission and backward compatibility with USB 3.2 and Thunderbolt 3/4.
Multi-channel data transmission, allowing alternate modes like DisplayPort output.
How to Examine a Diagram for USB-C Identification
Check the total pin count: If there are only 4 essential pins, it is USB 2.0. If SuperSpeed channels exist, it could be USB 3.0 or higher.
Look for TX/RX differential signal pairs: USB 2.0 lacks these, while USB 3.0 and USB 4.0 include at least 4-8 such signal pairs.
Analyze the Vbus/GND design: Higher versions may feature reinforced power delivery for stronger output capabilities.
Summary
By examining the pin layout on a diagram, you can distinguish between USB-C 2.0, 3.0, and 4.0. A basic 4-pin design indicates USB 2.0, while SuperSpeed data channels suggest USB 3.0 or higher. A full 24-pin setup is characteristic of USB 4.0, providing superior data transfer rates and power management.
